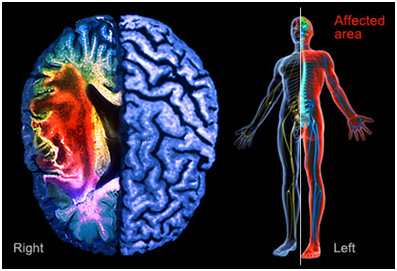
 Central pain (CP) is defined by the International Association for the Study of Pain as pain initiated or caused by a primary lesion or dysfunction in the central nervous system . The most common central pain conditions are central post-stroke pain , central pain in multiple sclerosis and central pain in spinal cord injury.
Central pain (CP) is defined by the International Association for the Study of Pain as pain initiated or caused by a primary lesion or dysfunction in the central nervous system . The most common central pain conditions are central post-stroke pain , central pain in multiple sclerosis and central pain in spinal cord injury.
Central post-stroke pain
Central post-stroke pain is often continuous and described as burning, aching, pricking, lacerating,and squeezing but may have any pain descriptor. Over two-thirds of central post-stroke pain patients have allodynia. Tactile, movement and cold allodynia are commonly found.
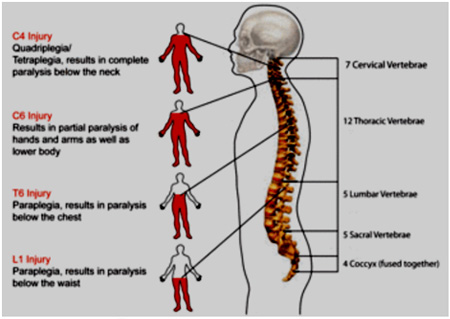 Spinal cord injury pain( SCI)
Spinal cord injury pain( SCI)
Central pain in SCI is often a spontaneous ongoing pain described as burning, squeezing, pricking/ sticking sensations. It may be accompanied by allodynia, in which non-noxious touch, thermal stimuli and movement can give rise to pain. Allodynia may occasionally be present without ongoing pain.
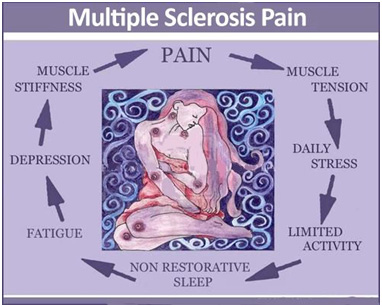 Central pain in multiple sclerosis (MS)
Central pain in multiple sclerosis (MS)
The demyelination seen in the central nervous system in MS is the likely cause of acute and chronic central pain conditions. Acute or chronic recurrent central pain conditions associated with MS disease include trigeminal neuralgia (TN), L'Hermitte's sign, painful tonic seizures and paroxysmal extremity pain. Most commonly, the patients report a chronic ongoing central pain mostly located in the lower extremities but pain may be widespread.
Treatment