 Knee pain can be caused by a sudden injury, an overuse injury, or by an underlying condition, such as arthritis.
Knee pain can be caused by a sudden injury, an overuse injury, or by an underlying condition, such as arthritis.
Knee pain is a common complaint that affects people of all ages
Symptoms
Causes of knee pain
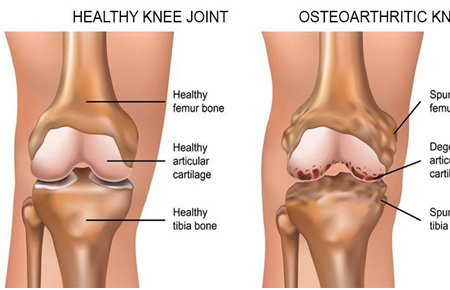 Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis
Arthritis is a chronic condition that causes joint inflammation. Symptoms include redness, warmth, swelling, tenderness and pain.
Common symptoms of osteoarthritis include pain, stiffness, tenderness, a limited range of motion and grating sensation when knee is bend. The pain is usually worse after activity.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis can affect joints on both sides of the body ( both knees, both hands, both wrists). In rheumatoid arthritis body's cells attack own tissues. Rheumatoid arthritis affects three to five times more women than men and often presents between the ages of 20 and 50 .
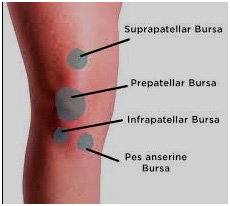 Bursitis
Bursitis
Bursitis is the inflammation of any of the fluid- filled sacs (bursae) protecting the body's joints. This is usually caused by repetitive motions or by a stress such as kneeling.
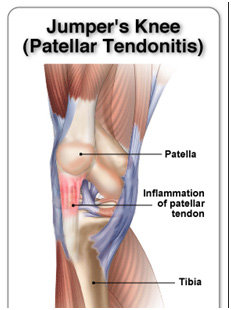 Tendonitis
Tendonitis
Tendonitis is a common sports injury caused by overuse of the same parts of the body. Patellar tendinitis or "jumper's knee" is an inflammation or irritation of tendon between the knee cap and the shin bone.
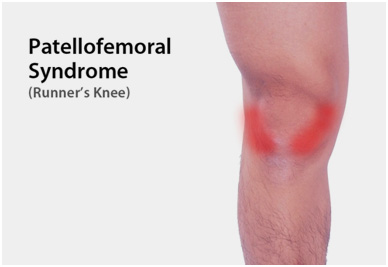 Patellofemoral pain syndrome(PFPS)
Patellofemoral pain syndrome(PFPS)
Knee pain or discomfort while walking up and down stairs, jumping or squatting may be symptoms of patellofemoral pain syndrome. This common knee problem is felt towards the front of the knee.
Injuries
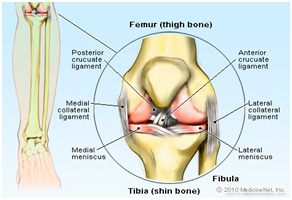
Knee injuries can be the result of sports, falls or trauma. They typically involve the ligaments that hold two of the bones of the knee-- the femur and tibia eg. ACL, MCL and Meniscal injuries.
Treatment options
Rest: When the knee is injured or is inflamed, as in bursitis, tendonitis or arthritis, it is important to rest the joint and avoid overuse. That mean keeping the knee straight (extended) or in positions that limits bending.
Ice/heat: Applying ice or cold packs to the knee can reduce inflammation and swelling, especially after an injury. Once swelling is gone, heat may be used to help relax and loosen tissues- although ice is the primary treatment.
Weight loss: Lose weight to reduce pressure on the knees.
Braces: Knee braces wrap around the knee and leg and help limit unwanted movement while supporting the knee. They are commonly used when knee ligaments are weak, and help to keep the knee from "buckling".
Pharmacology therapy
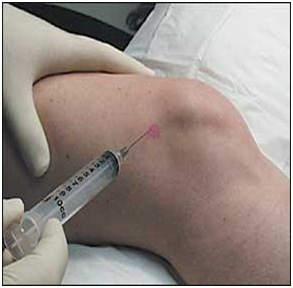
Injections in the knee joint: Platelets Rich Plasma(PRP), Ozone gas, Viscosupplement
Radiofrequency of Genicular. nerve